Triangular arbitrage is a strategy used to exploit inefficiencies in the currency markets by executing a series of trades across three currencies in different markets. Let’s assume we now observe the following quotes for currency pairs from the interbank market and dealers. We want to analyse whether there is any arbitrage opportunity.
Interbank Market Quotes
- CAD/USD – 1.3199/1.3201
- JPY/USD – 105.39/105.41
Dealer Quotes
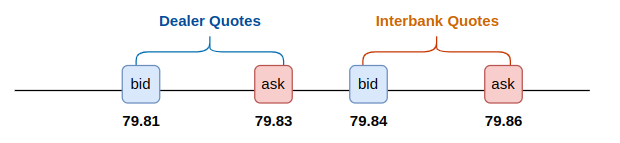
- JPY/CAD – 79.81/79.83
There are two methods for analysing triangular arbitrage.
Method 1
For the first method, assuming we borrow 1 USD, we can first buy CAD from the interbank market at the exchange rate of CAD/USD (1.3199/1.3201), obtaining 1.3199 CAD. Since we are buying CAD using USD and the USD is the base currency in the CAD/USD pair, we are effectively shorting the CAD/USD pair. Therefore, we need to use the bid price offered by the interbank market for the conversion.
With the CAD, we go to the dealer and buy JPY using the dealer quote for JPY/CAD (79.81/79.83). Using the 1.3199 CAD, we obtain 105.3412 JPY. This JPY is then used to buy back USD from the interbank market at the market quote for JPY/USD (105.39/105.41). Since we are buying USD using JPY, we need to convert the currency pair from JPY/USD to USD/JPY (0.009487/0.009489), which can be calculated using the following formula:
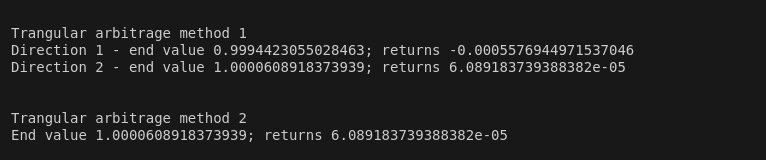
In the end, we receive 0.99937 USD for our initial investment of 1 USD, resulting in a loss. Therefore, this currency conversion route is not viable. The entire process can be represented by the following formula:
Now, let’s try the reverse direct, instead of USD -> CAD -> JPY, we go USD -> JPY -> CAD this time.
This route can be represented as the following formula:
After traversing the route in the same way as before, the USD amount we obtain at the end is 1.000063, representing a profit from our initial investment of 1 USD.
Next, let’s explore how to replicate this process in Python. First, we create dictionaries to store interbank quotes and dealer quotes.
We also need to create the reverse_exchange_rate function to switch the currencies in a currency pair, which is required for our calculations, such as converting JPY/USD to USD/JPY as mentioned earlier.
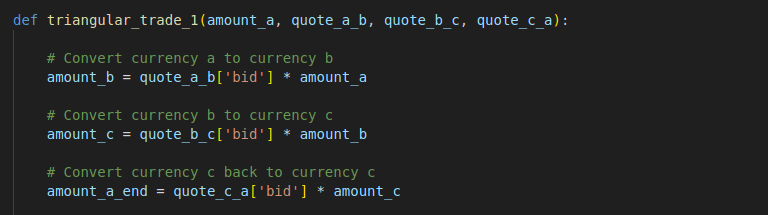
We create the triangular_trade_1 function to replicate the triangular arbitrage process for Method 1. This function takes the quotes of the currency pairs and performs conversions in sequence. It is designed to be generic, with no dependency on specific currency pairs or trade route direction, as these can be defined outside the function and passed in as parameters.
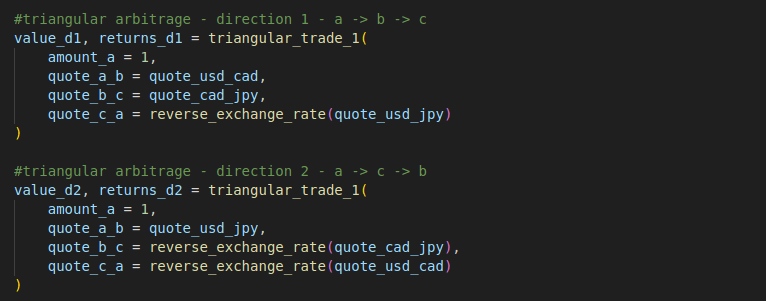
For example, these are the parameters defined for the triangular arbitrage processes described above. The executable full version of code can be found at bottom of this page.
Method 2
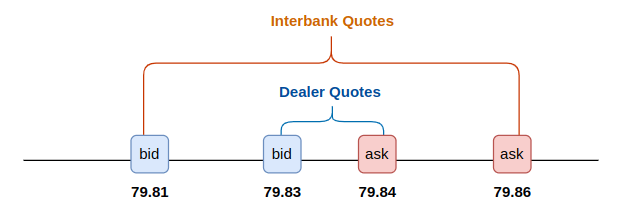
For Method 2, instead of traversing the currency triangle, we can directly derive the implied cross-rate currency pair, in our example, the JPY/CAD pair in the interbank market, based on the quotes of JPY/USD and CAD/USD:
For our example, the implied JPY/CAD pair in the interbank market is 79.84/79.86. Since the JPY/CAD pair quoted by the dealer is 79.81/79.83, the ask price quoted by the dealer (i.e., the price for buying from the dealer) is lower than the bid price quoted in the interbank market (i.e., the price for selling to the interbank market). This allows us to profit by longing the JPY/CAD pair from the dealer and shorting it in the interbank market.
One thing to note is that the arbitrage opportunity only exists when the ask price in one market is lower than the bid price in another market. Otherwise, the price at which you buy from one market is higher than the price at which you sell to another market, resulting in negative returns, as shown in the two scenarios below.
To replicate Method 2, the function triangular_trade_2 is created. This function first calculates the implied bid and ask prices of the cross-rate pair and then computes the returns for the arbitrage opportunity.
Here are the outputs of the two methods, showing that the returns are the same for both methods (Direction 2 of Method 1 and Method 2).
Full Code – Python
def triangular_trade_1(amount_a, quote_a_b, quote_b_c, quote_c_a):
# Convert currency a to currency b
amount_b = quote_a_b['bid'] * amount_a
# Convert currency b to currency c
amount_c = quote_b_c['bid'] * amount_b
# Convert currency c back to currency c
amount_a_end = quote_c_a['bid'] * amount_c
# Calculate returns
returns = (amount_a_end - amount_a) / amount_a
return amount_a_end, returns
def triangular_trade_2(amount_a, quote_a_b, quote_a_c, quote_b_c):
# Calculate implied quote_b_c
quote_b_c_implied_bid = reverse_exchange_rate(quote_a_b)['bid'] * quote_a_c['bid']
quote_b_c_implied_ask = reverse_exchange_rate(quote_a_b)['ask'] * quote_a_c['ask']
if quote_b_c_implied_bid > quote_b_c['ask']:
returns = (quote_b_c_implied_bid / quote_b_c['ask']) - 1
elif quote_b_c['bid'] > quote_b_c_implied_ask:
returns = (quote_b_c['bid'] / quote_b_c_implied_ask) - 1
else:
returns = 0
return amount_a * (1 + returns), returns
def reverse_exchange_rate(quote_a_b):
quote_b_a = {
'bid': 1 / quote_a_b['ask'],
'ask': 1 / quote_a_b['bid']
}
return quote_b_a
# Initial amount of currency A (USD)
initial_usd = 1
#interbank quotes
quote_usd_jpy = {'bid': 105.39, 'ask': 105.40}
quote_usd_cad = {'bid': 1.3199, 'ask': 1.3201}
#dealer quotes
quote_cad_jpy = {'bid': 79.81, 'ask': 79.83}
#triangular arbitrage - direction 1 - a -> b -> c
value_d1, returns_d1 = triangular_trade_1(
amount_a = 1,
quote_a_b = quote_usd_cad,
quote_b_c = quote_cad_jpy,
quote_c_a = reverse_exchange_rate(quote_usd_jpy)
)
#triangular arbitrage - direction 2 - a -> c -> b
value_d2, returns_d2 = triangular_trade_1(
amount_a = 1,
quote_a_b = quote_usd_jpy,
quote_b_c = reverse_exchange_rate(quote_cad_jpy),
quote_c_a = reverse_exchange_rate(quote_usd_cad)
)
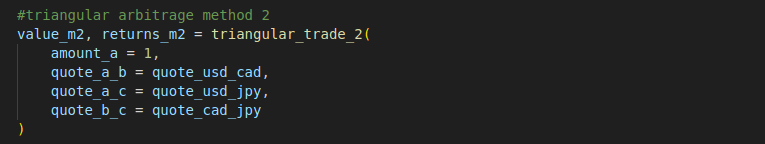
#triangular arbitrage method 2
value_m2, returns_m2 = triangular_trade_2(
amount_a = 1,
quote_a_b = quote_usd_cad,
quote_a_c = quote_usd_jpy,
quote_b_c = quote_cad_jpy
)
# Triangular arbitrage method 1
print('nn')
print(f'Trangular arbitrage method 1')
print(f'Direction 1 - end value {value_d1}; returns {returns_d1}')
print(f'Direction 2 - end value {value_d2}; returns {returns_d2}')
# Triangular arbitrage method 2
print(f'Trangular arbitrage method 2')
print(f'End value {value_m2}; returns {returns_m2}')
print('nn')