In CFA Fixed Income curriculum, module 3, section 3, “Effect of Interest Rate Volatility”, the impact of interest rate volatility on the value of callable and putable bonds is explored. In this blog post, I will replicate the examples from the CFA curriculum using Python code, leveraging the QuantLib library for bond valuations, including:
- Effect of interest rate volatility on callable bond
- Effect of interest rate volatility on putable bond
- Effect of yield curve level on callable bond
- Effect of yield curve level on putable bond
To replicate those examples, the code from the previous blog post will be reused for pricing callable and putable bonds. For more details, please refer to the earlier post
Effect of interest rate volatility on callable bond
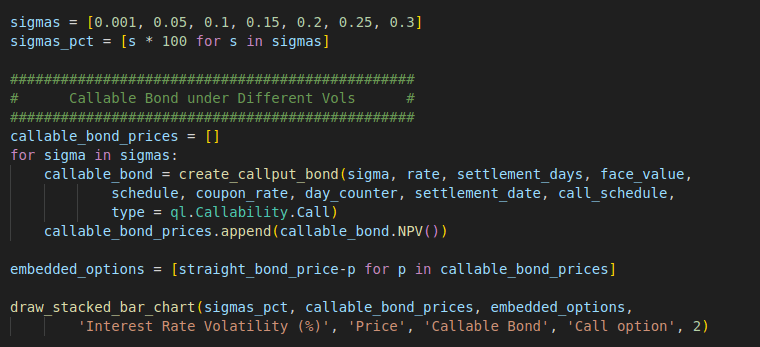
The first example discusses how interest rate volatility affects a callable bond. To replicate the example, we can define a list of volatilities to test, ranging from 0.1% to 30%. For each volatility, we create a corresponding callable bond (using the create_callput_bond function from the earlier blog post) and calculate its price. Additionally, we also create the equivalent straight (option-free) bond.
By comparing the straight bond price and the callable bond price, we can derive the value of the call option.
Call option = Straight bond – Callable bond
Eventually, we display the results as a stacked bar chart, where the bottom blue portion represents the value of the callable bond, the upper orange portion represents the value of the call option, and the entire bar represents the value of the straight bond.
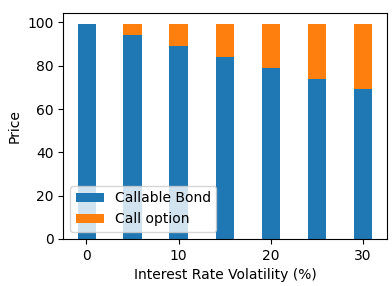
The first observation from the chart is that the straight bond prices remain the same across all levels of interest rate volatility, indicating that the value of an option-free bond is unaffected by interest rate volatility.
Secondly, the value of the callable option increases as interest rate volatility rises. It is easy to understand that higher volatility amplifies the likelihood of significant changes in interest rates, making it more probable that the option will be exercised.
Thirdly, the value of the callable bond decreases as interest rate volatility rises. A callable bond benefits issuers and causes a loss to bondholders. When the bond is called, the bondholder is forced to reinvest at potentially lower rates, leading to a loss of future interest income. As the possibility of early exercise increases, the value of the bond decreases for the bondholder.
Effect of interest rate volatility on putable bond
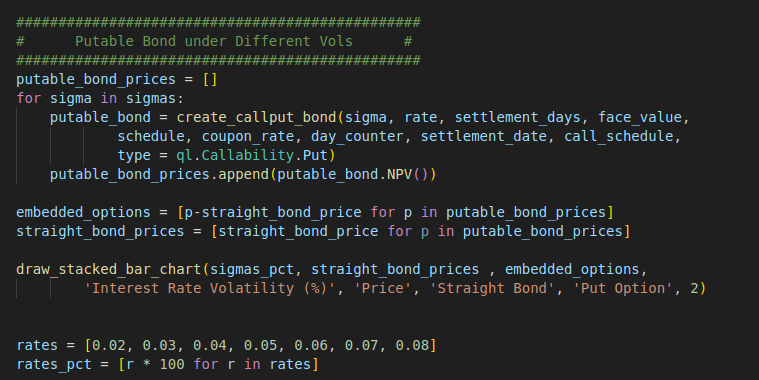
The second example discusses how interest rate volatility affects a putable bond. Similarly, we first create a putable bond for each volatility level and calculate the price of each.
The embedded put option can be derived from the price of the putable bond minus the price of the equivalent straight bond.
Put option = Putable bond – Straight bond
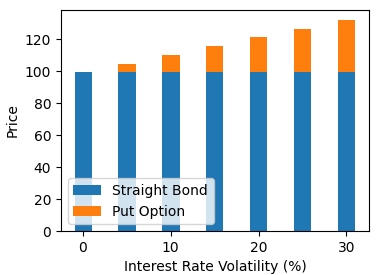
From the output chart, we can observe that the value of the putable option increases as interest rate volatility rises. This is consistent with the behavior of a callable bond. Higher volatility amplifies the likelihood of significant changes in interest rates, both upward and downward, making it more probable that the option will be exercised.
Unlike a callable bond, the value of a putable bond increases as interest rate volatility rises. A putable bond benefits bondholders and causes a loss to issuers. The rise of the embedded putable option value increase the value of the putable bond held by the bondholders.
Effect of yield curve level on callable bond
The third example discusses how interest rates affect a putable bond. To replicate the example, we define a list of interest rates, ranging from 2% to 8%, and create a putable bond and an equivalent straight bond for each rate.
For each rate, we calculate the callable bond price and the straight bond price, and then derive the value of the corresponding embedded call option.
From the output chart, we can observe that the price of the callable bond decreases as interest rates rise, which is expected since interest rates are used to discount the bond price. At the same time, the value of the embedded call option also decreases. This is because as interest rates increase, they move further away from the pre-agreed call price, reducing the likelihood that the call option will be exercised, and therefore lowering its value.
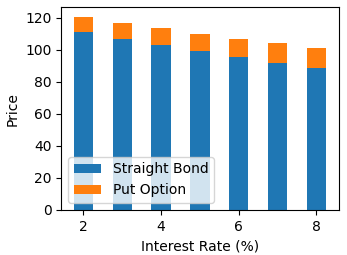
Effect of yield curve level on putable bond
The fourth example discusses how interest rates affect a putable bond. The code used to replicate the example and the output results are similar to those of the third example. The main difference is that the value of the embedded put option increases as interest rates rise. This is easy to understand, as the increase in interest rates moves the market price closer to the pre-agreed put price, thereby increasing the likelihood that the put option will be exercised.
Full Code – Python
import QuantLib as ql
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# Crate callability schedule
def create_call_schedule(schedule, type):
call_schedule = ql.CallabilitySchedule()
for c in schedule:
call_price = ql.BondPrice(c[1], ql.BondPrice.Clean)
call_schedule.append(
ql.Callability(
call_price,
type,
c[0]
)
)
return call_schedule
# Fit yield curve
def fit_yield_curve_handle(rate, evaluate_date):
curve = ql.FlatForward(evaluate_date, rate, ql.Actual360())
return ql.YieldTermStructureHandle(curve)
# function to create callable bond instance
def create_callput_bond(sigma, rate, settlement_days, face_value, schedule, coupon_rate,
day_counter, settlement_date, call_schedule, type):
curve_handle = fit_yield_curve_handle(rate, settlement_date)
# Use Hull White model for interest rates modeling
model = ql.HullWhite(curve_handle, a=0.01, sigma=sigma)
# Create callable Fixed-Rate bond instance
bond = ql.CallableFixedRateBond(
settlement_days,
face_value,
schedule,
[coupon_rate],
day_counter,
ql.Following,
face_value,
settlement_date,
create_call_schedule(call_schedule, type))
engine = ql.TreeCallableFixedRateBondEngine(model, 100)
bond.setPricingEngine(engine)
return bond
# create the straight bond instance
def create_straight_bond(rate, settlement_days, settlement_date, face_value, schedule, coupon_rate,
day_counter):
curve_handle = fit_yield_curve_handle(rate, settlement_date)
straight_bond = ql.FixedRateBond(
settlement_days,
face_value,
schedule,
[coupon_rate],
day_counter)
straight_engine = ql.DiscountingBondEngine(curve_handle)
straight_bond.setPricingEngine(straight_engine)
return straight_bond
# Function to plot stacked bar chart
def draw_stacked_bar_chart(x, y1, y2, x_label, y_label, y1_label, y2_label, width):
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.bar(x, y1, label=y1_label, width=width)
ax.bar(x, y2, bottom=y1, label=y2_label, width=width)
ax.set_xlabel(x_label)
ax.set_ylabel(y_label)
ax.set_title('')
ax.legend(loc='lower left')
plt.show()
# Set evaluation date for QuantLib
today = ql.Date(23, 12, 2024)
ql.Settings.instance().evaluationDate = today
# Define the bond
face_value = 100
coupon_rate = 0.05
settlement_date = ql.Date(15, 12, 2024)
settlement_days = 1
maturity_date = ql.Date(15, 12, 2028)
calendar = ql.UnitedStates(ql.UnitedStates.NYSE)
day_counter = ql.ActualActual(ql.ActualActual.Bond)
payment_freq = ql.Annual
# Define the cashflow schedule
schedule = ql.Schedule(
settlement_date,
maturity_date,
ql.Period(payment_freq),
calendar,
ql.Unadjusted,
ql.Unadjusted,
ql.DateGeneration.Backward,
False
)
rate = 0.05
straight_bond = create_straight_bond(rate, settlement_days, settlement_date, face_value, schedule,
coupon_rate, day_counter)
straight_bond_price = straight_bond.NPV()
# Define the callability schedule
call_schedule=[
(ql.Date(15, 12, 2026), 100),
(ql.Date(15, 12, 2027), 100),
]
sigmas = [0.001, 0.05, 0.1, 0.15, 0.2, 0.25, 0.3]
sigmas_pct = [s * 100 for s in sigmas]
################################################
# Callable Bond under Different Vols #
################################################
callable_bond_prices = []
for sigma in sigmas:
callable_bond = create_callput_bond(sigma, rate, settlement_days, face_value,
schedule, coupon_rate, day_counter, settlement_date, call_schedule,
type = ql.Callability.Call)
callable_bond_prices.append(callable_bond.NPV())
embedded_options = [straight_bond_price-p for p in callable_bond_prices]
draw_stacked_bar_chart(sigmas_pct, callable_bond_prices, embedded_options,
'Interest Rate Volatility (%)', 'Price', 'Callable Bond', 'Call option', 2)
################################################
# Putable Bond under Different Vols #
################################################
putable_bond_prices = []
for sigma in sigmas:
putable_bond = create_callput_bond(sigma, rate, settlement_days, face_value,
schedule, coupon_rate, day_counter, settlement_date, call_schedule,
type = ql.Callability.Put)
putable_bond_prices.append(putable_bond.NPV())
embedded_options = [p-straight_bond_price for p in putable_bond_prices]
straight_bond_prices = [straight_bond_price for p in putable_bond_prices]
draw_stacked_bar_chart(sigmas_pct, straight_bond_prices , embedded_options,
'Interest Rate Volatility (%)', 'Price', 'Straight Bond', 'Put Option', 2)
rates = [0.02, 0.03, 0.04, 0.05, 0.06, 0.07, 0.08]
rates_pct = [r * 100 for r in rates]
################################################
# Callable Bond under Different Rates #
################################################
callable_bond_prices = []
straight_bond_prices = []
embedded_options = []
for rate in rates:
callable_bond = create_callput_bond(0.1, rate, settlement_days, face_value,
schedule, coupon_rate, day_counter, settlement_date, call_schedule,
type = ql.Callability.Call)
callable_bond_price = callable_bond.NPV()
callable_bond_prices.append(callable_bond_price)
straight_bond = create_straight_bond(rate, settlement_days, settlement_date,
face_value, schedule, coupon_rate, day_counter)
straight_bond_price = straight_bond.NPV()
straight_bond_prices.append(straight_bond_price)
embedded_options.append(straight_bond_price - callable_bond_price)
draw_stacked_bar_chart(rates_pct, callable_bond_prices, embedded_options,
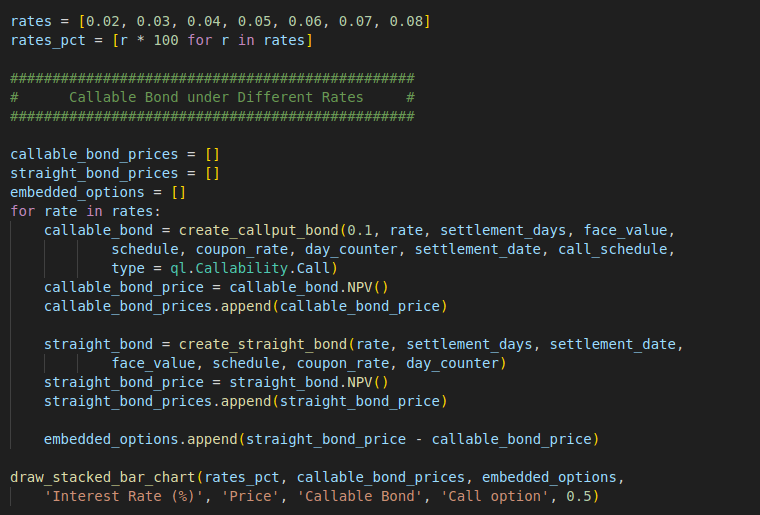
'Interest Rate (%)', 'Price', 'Callable Bond', 'Call option', 0.5)
################################################
# Putable Bond under Different Rates #
################################################
putable_bond_prices = []
straight_bond_prices = []
embedded_options = []
for rate in rates:
putable_bond = create_callput_bond(0.1, rate, settlement_days, face_value,
schedule, coupon_rate, day_counter, settlement_date, call_schedule,
type = ql.Callability.Put)
putable_bond_price = putable_bond.NPV()
putable_bond_prices.append(putable_bond_price)
straight_bond = create_straight_bond(rate, settlement_days, settlement_date,
face_value, schedule, coupon_rate, day_counter)
straight_bond_price = straight_bond.NPV()
straight_bond_prices.append(straight_bond_price)
embedded_options.append(putable_bond_price - straight_bond_price)
draw_stacked_bar_chart(rates_pct, straight_bond_prices , embedded_options,
'Interest Rate (%)', 'Price', 'Straight Bond', 'Put Option', 0.5)